News
Robotic Process Automation: What is a software robot good for?
What does RPA mean? What is a software robot?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) provides advanced technology to help you simplify routine office workflow tasks.
Its main goal is to automate various, often repetitive, rule-based activities and processes to complement, assist, and increase value-added activities of employees.
Software robots are able to perform predefined tasks and execute instructions according to specific rules. They can work in the background, on servers, or on personal computers too. It equals to an alive administrator at work: using the computer's graphical interface, the robot moves the cursor and is able to do whatever a person does on a screen or in an application.
Software robots work as virtual people, even using their own username and password to be able to use company software.
Currently, there are several RPA software available, which look similar from the outside, but with more or less different functionality and individual features under the surface.
 What can a software robot be really used for? How to implement automation?
What can a software robot be really used for? How to implement automation?
In the industrial world, physical robots are performing more and more repetitive, monotonous routine tasks in an increasing rate. Software robots, on the other hand, replace the human workforce in office and administrative environments, simplifying and accelerating work.
It is best to automate tasks that are done frequently, always in a standard way. This technology is most effective in automating low complexity, often repetitive, rule-based processes/process steps /activities with few exceptions.
Robots can effectively perform the following tasks:
- Retrieve, record, and manage data in various ways.
- Cut out text, paste it, fill in forms.
- Edit Excel spreadsheets.
- Keep track of data changes and send notifications.
- Save data and files.
- Read, analyse, write and send emails, open attachments and save them.
- Log on to websites and applications.
- Collect structured information from web pages, compare read data, transfer to another application.
- Utilize a user interface developed for people.
- Perform transactions.
- Perform counting, calculations, estimates.
- Transfer data between systems where direct interface or SOA (ESB) development is not available or feasible (e.g. between specialized systems and basic systems).
- Create files or modify them according to specific rules.
- Scan an invoice and record the data in accounting softwares, etc.
The list above could be continued for a long, since there are many processes/process stages that are suitable for automation in different areas of companies (e.g. finance, accounting, HR, IT, sales, supply chains…).
However, it is good to clarify that not all tasks can be performed by a software robot, and that not all tasks are meant to be automated. There are different aspects that can be used to evaluate how well a task can be automated, taking into account the
- degree of complexity,
- the potential savings of robotization,
- the automation potential,
- company priorities and last, but not least
- the current limitations of software robots.
It is definitely a good idea for companies to design their RPA strategy as a first step rather than making a random decision without immersing deeper in the subject.
The basis for developing the RPA strategy is a high-level overview and classification of existing processes in terms of automation. Strategy preparation itself consists of the following 4 main steps:
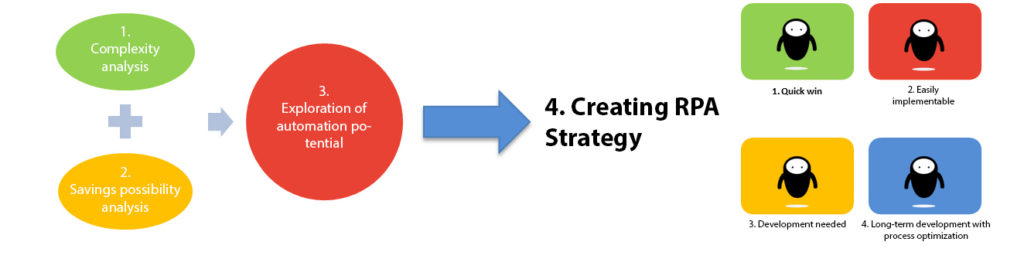
As part of step 4, a priority setting is made based on a roadmap, which is created to implement the automation of the various processes, taking into account the average turnaround times for each category of process automation (e.g. quick win, longterm development with process optimization).
When putting in practice the RPA strategy, it’s essential to know that the implementation of tasks that are consistent with each category of process automation will only guarantee the success of the implementation.
 What are the main features and advantages of software robots?
What are the main features and advantages of software robots?
Their application is not industry-specific: they can be used in almost any field to replace large numbers of human tasks, i.e. to perform repetitive processes on a regular basis.
Advantages:
- Robots are able to work 24 hours a day, on many different processes.
- They work accurately: they can eliminate errors, as a robot can work with a 0% error rate.
- Compliance can be ensured in the course of their tasks: Software robots will adhere to the rules that have been set for them when implementing automation.
- Business speed increases customer satisfaction: they work much faster than humans do, reducing the lead time of a particular process.
- The technology can be implemented quickly and at low cost, building on existing systems and processes as long as they run optimally.
- There is no need to replace or upgrade existing systems either.
- Robots can be parameterized in detail for almost any application, web sites, etc.
- Easy to scale, ensuring flexibility in operation.
- The end result of the robotic activity can be well controlled.
- Increased productivity gains (increase in the number of renders per unit time as the process cycle time and average treatment time decrease).
- They can bring significant cost savings.
- By replacing monotonous tasks, employees can engage in more creative activities, thereby improving their work morale and motivation.
- The robot can work with other robots, e.g. with a chat bot.
 Using software robots can also significantly reduce administrative costs. However, it should be kept in mind that the extension of automation depends largely on the area in which the technology is being applied. Cost reductions can range from 10% to 90%, but for a more accurate estimation, the processes/process steps you want to automate needs to be explored in detail.
Using software robots can also significantly reduce administrative costs. However, it should be kept in mind that the extension of automation depends largely on the area in which the technology is being applied. Cost reductions can range from 10% to 90%, but for a more accurate estimation, the processes/process steps you want to automate needs to be explored in detail.
Disadvantages:
- Danger of unemployment: From a certain perspective, RPA is a double-edged sword. Routine tasks can be automated, thus reducing the need for human input. However, workers employed for repetitive tasks are more likely to lose their jobs. (To avoid this, companies using software robots are reallocating available resources to areas with resource scarcity and providing retraining opportunities for their employees.)
- Complexity of implementation: RPA is still in the early stages of innovation, so introducing it into the production environment can be challenging, especially when establishing links with legacy systems. For some implementation projects, RPA initially seemed promising, but ultimately failed to deliver the desired business results, though this was often due to robotization of RPA-inappropriate processes, automation of suboptimal processes, or misunderstandings due to inadequate depth of specification.
- There is a limited opportunity for Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) at this technology. However, software robot developer companies are working on the integration of these robots.
- It is not recommended to use a software robot to handle unstructured data.
- Only people are currently able to solve complex, unique problems in a creative, effective way.
In addition to the disadvantages, it is also important to keep in mind the following statements:
- Break down the tasks to be robotized into small steps and prepare the robot for every possible event (e.g. pop-up window, missing data).
- If something is ignored, the process can easily go wrong; the robot will not continue its tasks, and in order to avoid this, it is extremely important to specify precisely and in detail the steps to be taken by the robot and to deal with all possible errors.
- Not all processes can be fully robotized.
- Supervision and human intervention may be required to carry out the processes, e.g. in the case of an error message, which is typical for exception branches.
- To understand, operate and develop systems, human resource remains essential.
Interesting facts
According to a study by Oxford Martin School (titled The Future of Employment), the following 10 financial jobs are likely to be taken over by robots in the future at a rate over 90%:
- bookkeeping, accounting clerk
- auditing clerk
- tax preparer
- payroll clerk
- timekeeping clerk
- billing clerk
- order clerk
- loan officer
- procurement clerk
- credit analyst
See a real softwer robot in action below in our demo video!
Sources:
4 percben: amit az RPA-ról tudni érdemes
Különbség a robotizált folyamatautomatizálás és a mesterséges intelligencia között
Robotizált folyamatautomatizálás
RPA: az irodákban is eljött az automatizáció kora
Miért nehéz a robotizáció, ha olyan egyszerű?
Robotizált folyamatautomatizálás – 7 megvalósult példa
Robotok pénzügyi munkakörökben
Hogyan dolgozzunk együtt gondolkodó robotokkal?
Szoftverrobotok a közigazgatásban
THE BENEFITS (AND LIMITATIONS) OF RPA IMPLEMENTATION
Pros & Cons Of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)

